
|
|
PDF HIP4086A Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | HIP4086A | |
| Descripción | 3-Phase MOSFET Driver | |
| Fabricantes | Intersil | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de HIP4086A (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 16 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
DATASHEET
80V, 500mA, 3-Phase MOSFET Driver
HIP4086, HIP4086A
The HIP4086 and HIP4086A (referred to as the HIP4086/A)
are three phase N-Channel MOSFET drivers. Both parts are
specifically targeted for PWM motor control. These drivers
have flexible input protocol for driving every possible switch
combination. The user can even override the shoot-through
protection for switched reluctance applications.
The HIP4086/A have a wide range of programmable dead
times (0.5µs to 4.5µs) which makes them very suitable for the
low frequencies (up to 100kHz) typically used for motor drives.
The only difference between the HIP4086 and the HIP4086A
is that the HIP4086A has the built-in charge pumps disabled.
This is useful in applications that require very quiet EMI
performance (the charge pumps operate at 10MHz). The
advantage of the HIP4086 is that the built-in charge pumps
allow indefinitely long on times for the high-side drivers.
To insure that the high-side driver boot capacitors are fully
charged prior to turning on, a programmable bootstrap refresh
pulse is activated when VDD is first applied. When active, the
refresh pulse turns on all three of the low-side bridge FETs
while holding off the three high-side bridge FETs to charge the
high-side boot capacitors. After the refresh pulse clears,
normal operation begins.
Another useful feature of the HIP4086/A is the programmable
undervoltage set point. The set point range varies from 6.6V to
8.5V.
Features
• Independently drives 6 N-Channel MOSFETs in three-phase
bridge configuration
• Bootstrap supply max voltage up to 95VDC with bias supply
from 7V to 15V
• 1.25A peak turn-off current
• User programmable dead time (0.5µs to 4.5µs)
• Bootstrap and optional charge pump maintain the high-side
driver bias voltage.
• Programmable bootstrap refresh time
• Drives 1000pF load with typical rise time of 20ns and fall
time of 10ns
• Programmable undervoltage set point
Applications
• Brushless Motors (BLDC)
• 3-phase AC motors
• Switched reluctance motor drives
• Battery powered vehicles
• Battery powered tools
Related Literature
• AN9642, “HIP4086 3-Phase Bridge Driver Configurations
and Applications”
• AN1829, “HIP4086 3-Phase BLDC Motor Drive
Demonstration Board, User Guide”
VDD
Speed
Controller
Brake
VDD
RDEL
AHI
ALI
BHI
BLI
CHI
CLI
CHB
BHB
AHB
AHO
BHO
CHO
CHS
BHS
AHS
VSS
ALO
BLO
CLO
Battery
24V...48V
FIGURE 1. TYPICAL APPLICATION
200
VxHB - VxHS = 10V
150
100
50
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C)
FIGURE 2. CHARGE PUMP OUTPUT CURRENT
March 27, 2015
FN4220.10
1
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774 |Copyright Intersil Americas LLC 2011, 2013, 2015. All Rights Reserved
Intersil (and design) is a trademark owned by Intersil Corporation or one of its subsidiaries.
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
1 page 
HIP4086, HIP4086A
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 7)
Supply Voltage, VDD Relative to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 16V
Logic Inputs (xLI, xHI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . GND - 0.3V to VDD + 0.3V
Voltage on xHS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -6V (Transient) to 85V (-40°C to +150°C)
Voltage on xHB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VxHS - 0.3V to VxHS +VDD
Voltage on xLO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VSS - 0.3V to VDD +0.3V
Voltage on xHO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VxHS - 0.3V to VxHB +0.3V
Phase slew rate (on xHS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20V/ns
Maximum Recommended Operating
Conditions
Supply Voltage, VDD Relative to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7V to 15V
Logic Inputs (xLI, xHI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0V to VDD
Voltage on xHB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VxHS + VDD
Voltage on xHS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0V to 80V
Ambient Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to +125°C
Junction Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to +150°C
RDEL range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10kΩ to 100kΩ
Thermal Information
Thermal Resistance (Typical)
JA (°C/W) JC (°C/W)
SOIC Package (Notes 4, 6) . . . . . . . . . . . . .
75
22
SOIC Package HIP4086AABZ (Notes 5, 6)
51
22
PDIP* Package (Notes 4, 6) . . . . . . . . . . . .
70
29
Storage Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-65°C to +150°C
Operating Junction Temp Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to +150°C
Pb-Free Reflow Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . see TB493
*Pb-free PDIPs can be used for through-hole wave solder processing only.
They are not intended for use in Reflow solder processing applications.
CAUTION: Do not operate at or near the maximum ratings listed for extended periods of time. Exposure to such conditions may adversely impact product
reliability and result in failures not covered by warranty.
NOTES:
4. JA is measured with the component mounted on a low effective thermal conductivity test board in free air. See Tech Brief TB379 for details.
5. JA is measured with the component mounted on a high effective thermal conductivity test board in free air. See Tech Brief TB379 for details.
6. For JC, the “case temp” location is taken at the package top center.
7. Replace x with A, B, or C.
DC Electrical Specifications VDD = VxHB = 12V, VSS = VxHS = 0V, RDEL = 20k, RUV = , Gate Capacitance (CGATE) = 1000pF, unless
otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply across the operating junction temperature range, -40°C to +150°C.
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
SUPPLY CURRENTS
VDD Quiescent Current
xHI = 5V, xLI = 5V (HIP4086)
xHI = 5V, xLI = 5V (HIP4086A)
VDD Operating Current
f = 20kHz, 50% Duty Cycle (HIP4086)
f = 20kHz, 50% Duty Cycle (HIP4086A)
xHB On Quiescent Current
xHI = 0V (HIP4086)
xHI = 0V (HIP4086A)
xHB Off Quiescent Current
xHB Operating Current
xHI = VDD (HIP4086)
xHI = VDD (HIP4086A)
f = 20kHz, 50% Duty Cycle (HIP4086)
f = 20kHz, 50% Duty Cycle (HIP4086A)
xHB, xHS Leakage Current
VxHS = 80V, VxHB = 93V
Charge Pump, HIP4086 only, (Note 8)
QPUMP Output Voltage
QPUMP Output Current
UNDERVOLTAGE PROTECTION
No Load
VxHS = 12V, VxHB = 22V
VDD Rising Undervoltage Threshold
VDD Falling Undervoltage Threshold
Minimum Undervoltage Threshold
RUV open
RUV open
RUV = VDD
TJ = +25°C
MIN MAX
(Note 9) TYP (Note 9)
TJ = -40°C TO +150°C
MIN
(Note 9)
MAX
(Note 9)
UNITS
2.7 3.4 4.2
2.3 2.4 2.6
6.3 8.25 10.5
3.1 3.6 4.1
- 40 80
80 100
0.6 0.8 1.3
0.8 0.9
1
0.7 0.9 1.3
0.8 0.9
1
7 24 45
2.1
2.1
5
2.8
-
0.5
0.7
-
-
-
4.3 mA
2.7 mA
11 mA
4.4 mA
100 µA
200 µA
1.4 mA
1.2 mA
2.0 mA
1.2 mA
50 µA
11.5
50
12.5
100
14
130
10.5
-
14.5
140
V
µA
6.2
5.75
5
7.1
6.6
6.2
8.0
7.5
6.8
6.1
5.6
4.9
8.1 V
7.6 V
6.9 V
Submit Document Feedback
5
FN4220.10
March 27, 2015
5 Page 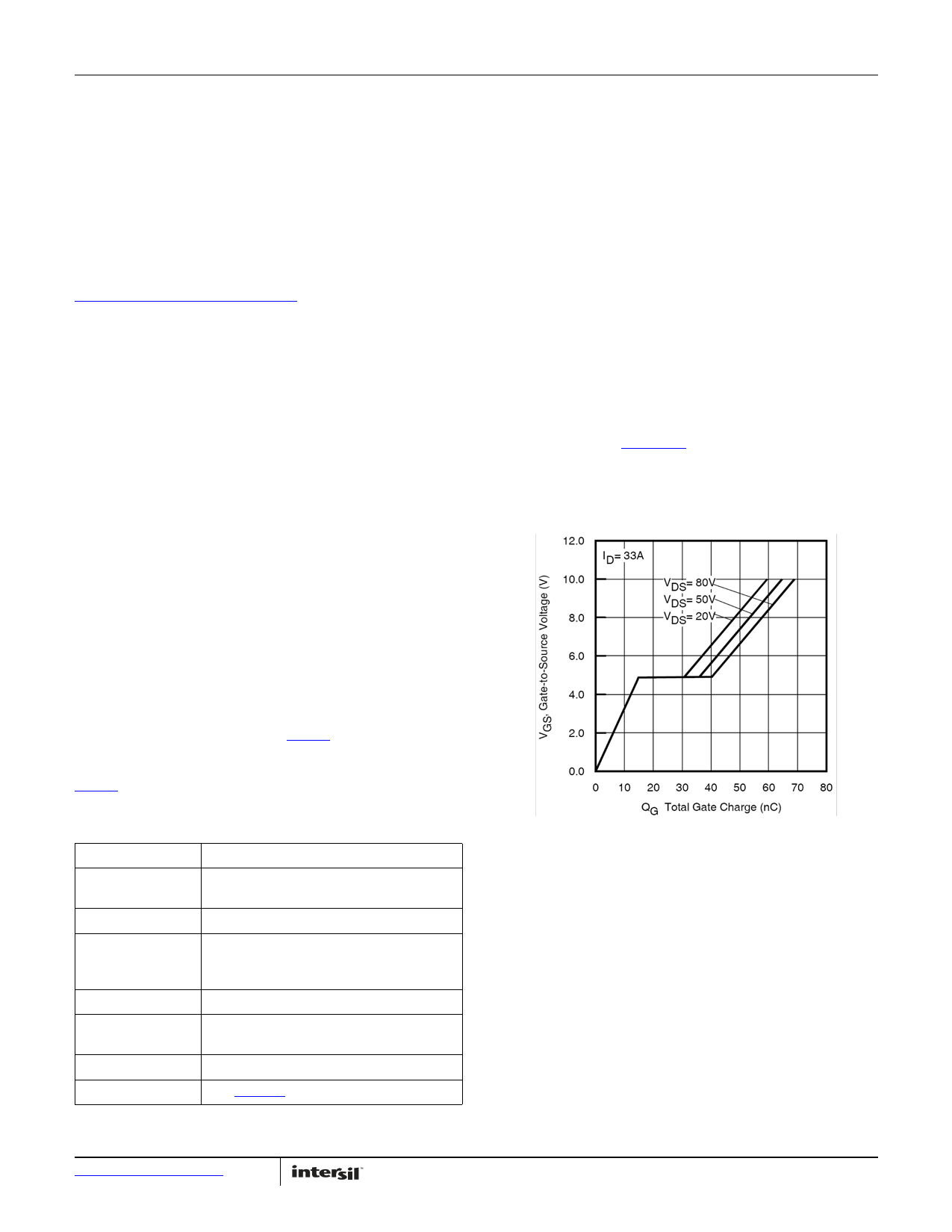
HIP4086, HIP4086A
Charge Pump
The internal charge pump of the HIP4086/A is used to maintain
the bias on the boot cap for 100% duty cycle. There is no limit for
the duration of this period. The user must understand that this
charge pump is only intended to provide the static bias current of
the high-side drivers and the gate leakage current of the
high-side bridge FETs. It cannot provide in a reasonable time, the
majority of the charge on the boot cap that is consumed, when
the xHO drivers source the gate charge to turn on the high-side
bridge FETs. The boot caps should be sized so that they do not
discharge excessively when sourcing the gate charge. See
“Application Information” on page 11 for methods to size the
boot caps.
The charge pump has sufficient capacity to source a worst-case
minimum of 50µA to the external load. The gate leakage current
of most power MOSFETs is about 100nA so there is more than
sufficient current to maintain the charge on the boot caps.
Because the charge pump current is small, a gate-source resistor
on the high-side bridge FETs is not recommended. When
calculating the leakage load on the outputs of xHS, also include
the leakage current of the boot capacitor. This is rarely a problem
but it could be an issue with electrolytic capacitors at high
temperatures.
Application Information
Selecting the Boot Capacitor Value
The boot capacitor value is chosen not only to supply the internal
bias current of the high-side driver but also, and more
significantly, to provide the gate charge of the driven FET without
causing the boot voltage to sag excessively. In practice, the boot
capacitor should have a total charge that is about 20 times the
gate charge of the driven power FET for approximately a 5% drop
in voltage after charge has been transferred from the boot
capacitor to the gate capacitance.
The following parameters shown in Table 1 are required to
calculate the value of the boot capacitor for a specific amount of
voltage droop when using the HIP4086/A (no charge pump). In
Table 1, the values used are arbitrary. They should be changed to
comply with the actual application.
TABLE 1.
VDD = 10V
VHB = VDD - 0.6V
= VHO
Period = 1ms
VDD can be any value between 7 and 15VDC.
High-side driver bias voltage (VDD - boot diode
voltage) referenced to VHS.
This is the longest expected switching period.
IHB= 100µA
Worst case high-side driver current when
xHO = high (this value is specified for VDD = 12V
but the error is not significant).
RGS = 100kΩ
Ripple = 5%
Gate-source resistor (usually not needed).
Desired ripple voltage on the boot cap (larger
ripple is not recommended).
Igate_leak = 100nA
Qgate80V = 64nC
From the FET vendor’s datasheet.
From Figure 21.
Equation 1 calculates the total charge required for the Period
duration. This equation assumes that all of the parameters are
constant during the Period duration. The error is insignificant if
Ripple is small.
QC = Qgate80V + Period (IHB + VHO RGS + Igate_leak)
Cboot = QC RippleVDD
Cboot = 0.52F
(EQ. 1)
If the gate to source resistor is removed (RGS is usually not
needed or recommended), then:
Cboot = 0.33µF
These values of Cboot will sustain the high side driver bias during
Period with only a small amount of Ripple. But in the case of the
HIP4086, the charge pump reduces the value of Cboot even
more. The specified charge pump current is a minimum of 50µA
which is more than sufficient to source Igate_leak. Also, because
the specified charge pump current is in excess of what is needed
for IHB, the total charge required to be sourced by the boot
capacitor is shown by Equation 2.
QC = Qgate80Vor Cboot = 0.13F
(EQ. 2)
Not only is the required boot cap smaller in value, there is no
restriction on the duration of Period.
FIGURE 21. TYPICAL GATE VOLTAGE vs GATE CHARGE
Submit Document Feedback 11
FN4220.10
March 27, 2015
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 16 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet HIP4086A.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| HIP4086 | 3-Phase MOSFET Driver | Intersil Corporation |
| HIP4086A | 3-Phase MOSFET Driver | Intersil |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
